|
|
|
Indian Pediatr 2015;52: 634 |
 |
Facial Angiofibromas
|
|
Abhijit Dutta, *Sudip Kumar Ghosh and
#Rajesh Kumar Mandal
From Departments of Pediatric Medicine and #Dermatology,
North Bengal Medical College; and *Dermatology, RG Kar Medical College;
Kolkata, West Bengal, India. [email protected]
|
|
A nine-year-old boy presented to us with recurrent episodes of
convulsions over the preceding two years. His family and birth history
was unremarkable. He had learning difficulties and poor scholastic
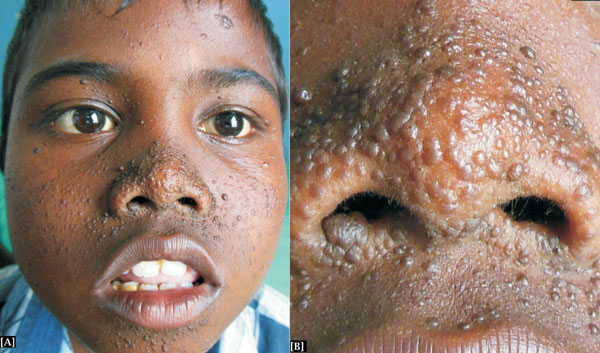
performance. Cutaneous examination revealed multiple non-tender, dark
brown and skin-coloured telangiectatic papules of varying size over the
face (Fig. 1). In addition, he had three oblong
hypopigmented macules over the upper back. Systemic examination
including ophthalmoscopy was normal. Computerized tomographic (CT) scan
of brain revealed multiple calcified subependymal nodules of different
size. Based on the features, a diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis was
established. Subsequent echocardiography and ultrasonography of the
abdomen were normal.
(a)
(b) |
|
Fig. 1 (a) Dark brown and skin-coloured papules of
varying size over the face; and (b) Close-up showing typical
lesions of angiofibromas.
|
The distinctive facial lesions in the present patient
were angiofibromas, also referred by a misnomer – adenoma sebaceum.
These are pink, dark brown, or skin-colored telangiectatic papules,
often observed in the nasolabial folds and on the cheeks and chin.
Pathologically, they are hamartomas, and composed of fibro-vascular
tissue. They usually present after 2 years of age and gradually increase
in size and number until adolescence. Besides tuberous sclerosis,
angiofibroma may also be seen in multiple endocrine neoplasia type I and
Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. Treatment of these skin lesions is usually
required for cosmetic concerns, and different forms of laser being the
best option.
Common differential diagnoses of angiofibroma
include, trichoepithlioma (small, firm, flesh-coloured papules, begin
during early puberty), acne (polymorphic lesions, presence of comedones,
also present in other acne-prone areas, usually noted during
adolescence), syringoma (small, skin-colored, dermal papules, typically
on the lower eyelid; occurs between 20 and 40 years of age), and
sebaceous hyperplasia (<3 mm yellowish telangiectatic papules with
central umbilication; common in elderly people)
|
|
|
 |
|